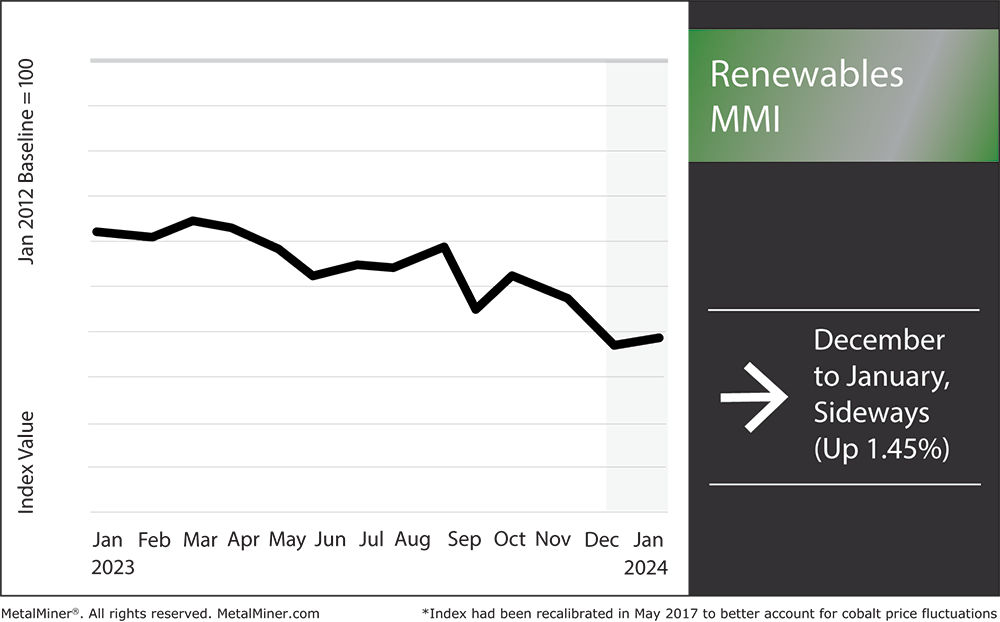
The Renewables index began 2023 fairly sideways. However, it broke that trend in Q3 and Q4 when it edged downward. Numerous components of the index, including silicon and cobalt, experienced market oversupply. This caused prices to drop and pulled the index down with it. Grain oriented electrical steel also experienced market volatility in Q3 and Q4, which massively impacted the index. While experts anticipate the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law will fuel renewable energy projects, the remaining oversupply of metals like cobalt and silicon will continue to put some bearish pressure on the index.
Month-over-month, the Renewables MMI (Monthly Metals Index) moved sideways, edging up by just 1.45%.
Renewables and grain oriented electrical steel markets could face massive obstacles in 2024. Opt into MetalMiner’s free weekly newsletter to get weekly metal market insights and start saving on COGS.
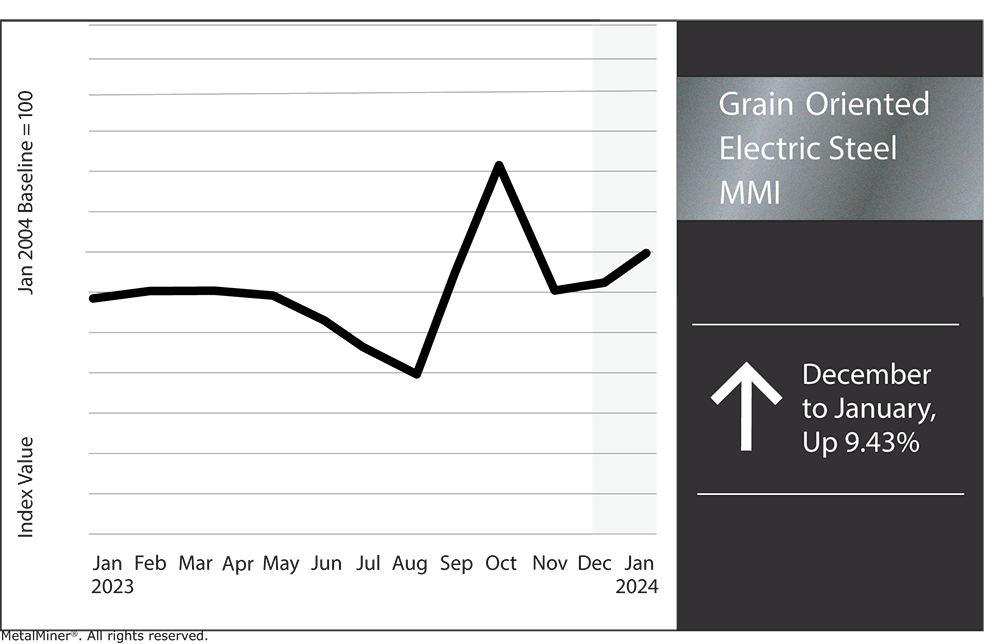
Grain Oriented Electrical Steel MMI
While U.S. GOES prices flattened around January 2, Chinese GOES prices began trading close to short-term support zones. Meanwhile, European GOES prices continue to trade well above short-term resistance zones. Furthermore, Japanese GOES experienced the largest 30-day price change, surging by 42.46%. This had the largest impact on the index overall, and ultimately the Grain Oriented Electrical Steel MMI rose by 9.43%.
Power Grids Still Short on Transformers
A recent article from Renewable Energy World shed some light on the ongoing transformer shortages in the U.S. In particular, the article highlighted why those much-needed transformers aren’t being built. The article speculates that RTO’s (regional transmission organizations) and ISOs (independent system operators) are partially responsible for the nation’s insufficient transmission capacity. 30 years ago, these organizations aimed to inject competition into an industry dominated by utilities. Now, however, there is much more to consider.
RTO’s bring together transmission owners, users, and other organizations approved by the Commission. Their mission is to actively coordinate the use and operation of electricity across, and sometimes between, various regions. RTOs manage wholesale power markets. This helps to ensure open access to transmission for all players while actively maintaining the reliability of the entire transmission network.

On the other hand, ISOs are the entities tasked with guaranteeing the dependability and effectiveness of the power infrastructure. They run the wholesale power markets, control the flow of electricity, and ensure system stability. In most cases, ISOs oversee and manage the grid, sometimes on a regional scale.
The Renewable Energy News article goes on to discuss how utilities often give priority to local transmission projects over regional and interregional ones. More importantly, they frequently avoid RTO or ISO interference with local planning. This narrow concentration might impede the wider grid’s development. Moreover, it comes on top of the extreme market volatility often seen with grain oriented electrical steel prices.
Receive monthly price trends for 10 different metal industries and use it as a sourcing reference point. Sign up for MetalMiner’s free monthly MMI report.
Solving Gaps Lying Between RTO’s/ISO’s and Local Transmission Projects
Inadequate coordination among local, regional, and inter-regional transmission planning can lead to inefficiencies and overlooked opportunities, many of which are critical to optimizing the electricity system in the United States.
According to an Electricity Markets and Policy Group report, The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) created rules for inter-regional cooperation and regional transmission planning. These are valuable to how regions manage their transmission needs. However, the study also highlights the difficulties inherent in identifying, quantifying, and implementing transmission advantages at the local, regional, and inter-regional levels.

Enhancing planning and coordination amongst local, regional, and inter-regional transmission projects proves crucial in solving the ongoing transformer shortage dilemma. To that point, there exists several potential remedies to the problem. The first involves establishing a minimal set of transmission advantages for evaluation, while the next focuses on modifying reliability measurements into a form that is consistent with economic benefits.
Organizations can also encourage more effective and efficient transmission development at various scales by ensuring public utility transmission providers use standard inter-regional cost allocation techniques. Finally, organizations can also consider closing regulatory gaps between state and federal regulators.
Renewables MMI: Notable Price Shifts
- Chinese silicon rose by 4.78%, bringing prices to $2,113.87 per metric ton.
- Cobalt cathodes also rose by 3.99%, despite oversupply globally. Prices at month’s start sat at $32,902.57 per metric ton.
- U.S. steel plate prices exhibited bullish action, increasing by 7%. This left prices at $1,452 per short ton.
- Lastly, Chinese neodymium prices dropped by a sharp 7.57% to $79,083.76 per metric ton.
Why gamble with your metal procurement costs? Trust MetalMiner’s track record and start saving on COGS. View our full metals forecasting catalog.




