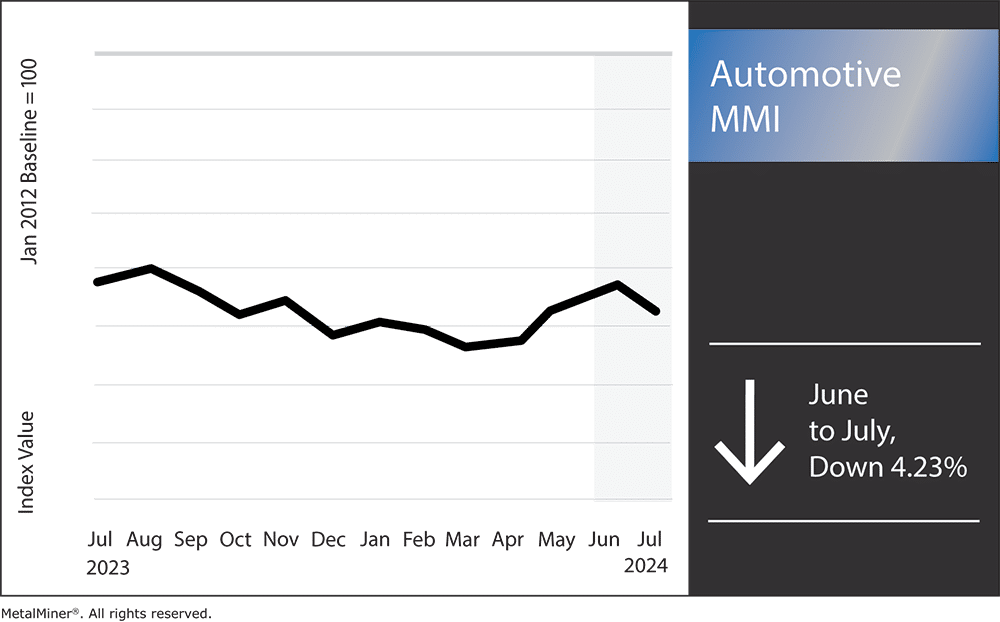
Month over month, the Automotive MMI (Monthly Metals Index) failed to break very far outside of its year-long sideways trend. All in all, the index dropped by 4.23% Numerous factors tugged the index down month-over-month, including slowing electric vehicle production. Another pressing matter putting pressure on the automotive market is China implementing further restrictions on rare earths exports. This includes restrictions on gallium and germanium, two metals vital for vehicle microchip manufacturing.
With the automotive market already experiencing a global shortage of microchips, automotive manufacturers will need to plan accordingly to offset these new export restrictions. Vital geopolitical news like this which impacts metal markets are covered weekly in MetalMiner’s newsletter.
EV Market Slows Down in the Second Half of 2024
The electric vehicle (EV) market, once characterized by rapid growth and optimism, is now facing significant slowdown in the second half of 2024. Despite earlier projections anticipating robust production and sales, various factors have converged to temper the market’s momentum.
Divergent consumer response to various EV brands is one of the primary issues. While some manufacturers continue to see record demand, others struggle to hold onto their market share because of concerns about perceived quality. Within the EV industry, this discrepancy creates a narrative of two marketplaces where success and failure live in sharp contrast.

The state of the economy also played a crucial role in the slowdown of EV production. Inflation and rising interest rates continue to decrease the purchasing power of customers, making expensive products like EVs less accessible. Consequently, the predicted surge in EV sales has not materialized as expected.
Automakers Hit the Brakes on Electric Vehicles
Several automakers recently revised their investment plans in reaction to current market conditions. For example, Volvo reduced financing for its electric vehicle programs, including its ownership of Polestar. This action is part of a larger trend among manufacturers to reduce or postpone expenditures connected to electric vehicles until market circumstances improve.
Along with this, the EV industry’s supply chain has experienced obstacles, especially with locating vital battery materials. These interruptions in the supply chain continue to raise production costs and cause delays, which have a negative impact on the general effectiveness and profitability of EV production.
EV Projections Remain Optimistic
In an effort to reduce expenses and better match production to the demands of the market, a number of automakers are either slowing down or postponing the launch of new facilities for electric vehicles. However, the long-term picture for the EV is still positive despite these setbacks. Many experts anticipate that advancements in battery technology, government incentives, and a growing public awareness of environmental problems will drive future expansion.
Get articles like this delivered monthly to your inbox with MetalMiner’s Monthly Metals Index report, which gives you monthly price trends for 10 different metal areas. Sign up here.
Will China’s Rare Earths Export Ban Threaten the U.S. Auto Industry?
The already-severe microchip scarcity in the U.S. automobile sector could worsen due to China’s recent move to impose export restrictions on essential rare earths. This action, which is a component of a larger plan in the continuing tech war between the U.S. and China, targets metals essential to producing semiconductors, including gallium, germanium, and graphite.
Meanwhile, companies continue to explore several workable alternatives to lessen the effects of these difficulties, and finding alternative sourcing strategies such as the ones covered in MetalMiner’s 5 Best Metal Sourcing Strategies. Many American businesses are looking into other sources of rare earth elements. Indeed, potential suppliers from nations like Canada and Australia might lessen dependency on Chinese exports. Furthermore, technology advancements and their application could help recover more rare earth elements from electronic trash. This strategy not only resolves supply-side problems but also advances sustainability.
How U.S. Trade Agreements Can Mitigate China’s Rare Earths Restrictions
Establishing strategic alliances with allies may help build a network of trustworthy suppliers and act as a safety net against supply chain interruptions. Meanwhile, trade agreements and cooperative initiatives can guarantee a consistent supply of necessary resources.
By using these tactics, the U.S. can effectively handle the difficulties brought about by China’s export prohibitions and strive toward a safer and more environmentally friendly automobile supply chain. Diversification, innovation, investment, and international collaboration are all necessary on the route ahead to reduce risks and guarantee the consistent manufacturing of microchips that are essential for contemporary automobiles.
Automotive MMI: Noteworthy Price Shift
Gain the upper hand in a dynamic market. MetalMiner Insights keeps you ahead of the curve, allowing you to anticipate price shifts and capitalize on unseen opportunities.
- Chinese lead rose in price by 3.84%, bringing prices to $2,666.05 per metric ton.
- Hot dipped galvanized steel dropped by 4.97%, leaving prices at $1,108 per short ton.
- LME copper (primary 3 month) fell 5.12%, which brought prices to $9,625 per metric ton.
- Finally, Korean aluminum 5052 coil premium over 1050 traded sideways, only dropping in price by 0.29% to $4.18 per kilogram.




