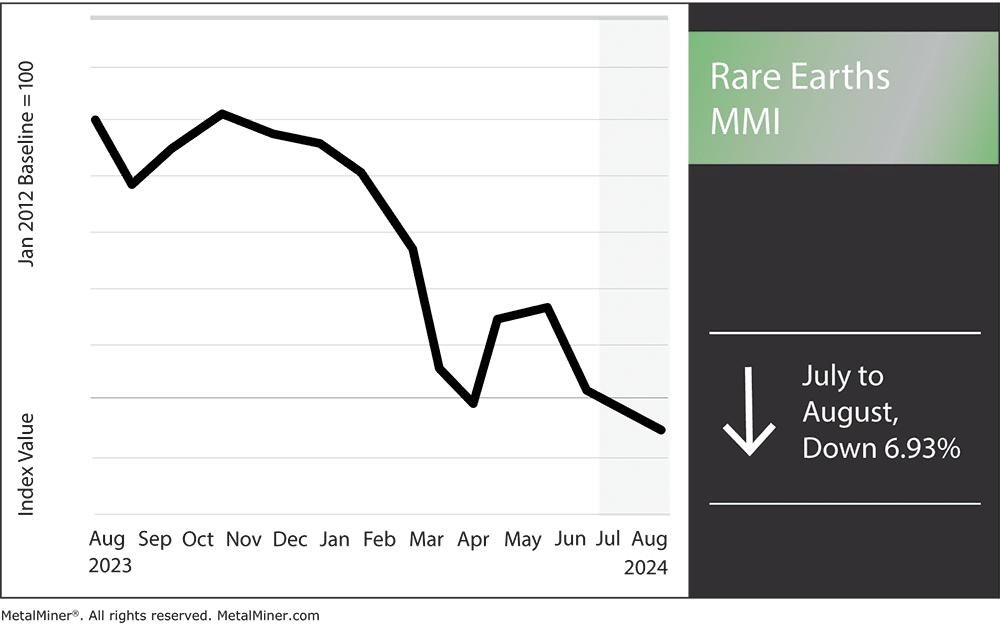
The bears continued to make their way into the Rare Earths MMI (Monthly Metals Index), with yet another drop in price action, this time by 6.93%. Many factors pulled at rare earths prices overall, including oversupply, weak demand for metals within China and shifting dynamics in global rare earths supplies. It seems China’s over-production of rare earths continues to contribute to a massive supply glut, leading to cheaper prices and bearish sentiment.
See why technical analysis is a superior forecasting methodology over fundamental analysis and why it matters for your rare earth purchases.
China’s Metal Demand Weakens: What It Means for U.S. Rare Earths Buyers
As the world’s biggest producer and consumer of several metals, any change in China’s domestic metal demand significantly impacts global supply chains. For this reason, there are concerns about the possible effects of recent reports showing a notable decline in China’s demand for metals on U.S. buyers of rare earths.
Fresh data from factories indicates a decline in China’s industrial landscape. The Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI) clearly demonstrates this trend, showing a decline in manufacturing activity and a resulting decrease in demand for metals. This slowdown partly results from China’s economy moving away from heavy industries and toward a more service-oriented model.

Changes in Chinese demand also have tremendous impacts on the rare earths industry. This is because China is the world’s largest producer and exporter of rare earths, in addition to being a major consumer of metals overall. If demand declines in China, it could lead to excess supply on the international market. In the short run, this could result in more predictable supply chains and more stable costs for U.S. consumers.
Receive indispensable updates on rare earth market shifts and price trends, empowering your company to make informed purchasing decisions. Opt into MetalMiner’s free weekly newsletter
Is Price Stability in Sight?
The U.S. continues to investigate substitute sources and invest in local manufacturing capabilities to lessen its reliance on Chinese rare earths suppliers. If Chinese demand continues to decline, U.S. buyers can diversify their supply sources and make domestic investments in more environmentally friendly mining techniques. Additionally, further reducing dependency on Chinese imports may quicken the advancement of recycling technologies.

The effect of China’s methods of rare earth mining on the environment is another factor to consider. After all, the environmental harm caused by China’s mining operations has long been a source of criticism. A decrease in Chinese demand may result in fewer mining operations, which could help the environment. In the long run, this might also pressure China to adopt more sustainable methods, which would be advantageous for the world economy.
All in all, buyers of rare earths in the U.S. face a mixed bag due to China’s declining demand for metals. Although it provides immediate advantages like pricing stability and a more predictable supply chain, it also highlights the necessity of making strategic changes in supply networks.
Will Rare Earths Prices Rise in the Remainder of 2024?
Rare earths prices appeared to be bottoming out earlier this year. According to a Reuters study, prices could rise in the second half of 2024, driven by wind power and electric vehicle demand.
Meanwhile, the need for praseodymium (PrNd) and neodymium (NeO), both necessary for producing the powerful magnets used in EV motors, has persisted. According to a recent analysis, there was a slower decrease in PrNd prices in the first half of 2024, which raised optimism for a market reversal.

Geopolitical conflicts and supply chain limitations continue to be major factors in the global rare earths market. China has also tightened export regulations, which will decrease the supplies worldwide. Prices will probably rise due to this move as businesses rush to protect their supply lines.
MetalMiner Insights is your key to risk-mitigating strategies, view our full catalog of covered metals.
Counterpoints to Increases in Rare Earth Prices
There are arguments that contradict these encouraging signs. A few market analysts recently issued a warning stating that the price increase may be driven more by sentiment than by fundamentals. Even if demand is rising, supply chain disruptions might not prove as bad as expected, which might restrain price increases. Furthermore, fresh mining projects and recycling programs are progressively going online, which may eventually relieve some supply constraints.
Ultimately, it is essential to temper expectations with the understanding that market sentiment and actual fundamentals may not always align perfectly. As with any commodity, a myriad of factors will influence the ultimate price trajectory, and stakeholders should remain vigilant and adaptable to these dynamic conditions.
Rare Earths MMI: Noteworthy Price Trends
Enjoy this article? MetalMiner’s monthly MMI report gives you price updates, market trends and industry insight for (METAL TYPE HERE) and 9 other metal industries. Sign up for free.
- Neodymium moved sideways, rising 2.32% to $62,690.77 per metric ton.
- Terbium oxide fell 6.85% to $689.77 per kilogram.
- Dysprosium oxide fell by 8.01% to $232.42 per kilogram.
- Finally, terbium metal fell the most month-over-month. In all, prices dropped by 8.16% to $854.42 per kilogram.




