Sign up for daily news updates from CleanTechnica on email. Or follow us on Google News!
We forecast the U.S. energy sector to emit about 4,790 million metric tons of carbon dioxide (CO2) in 2023, a 3% decrease from 2022. Much of this decline results from lower electricity generation from coal-fired power plants due to higher generation from renewable sources such as solar power. We expect this trend to continue into 2024, with CO2 emissions declining 1% relative to 2023.
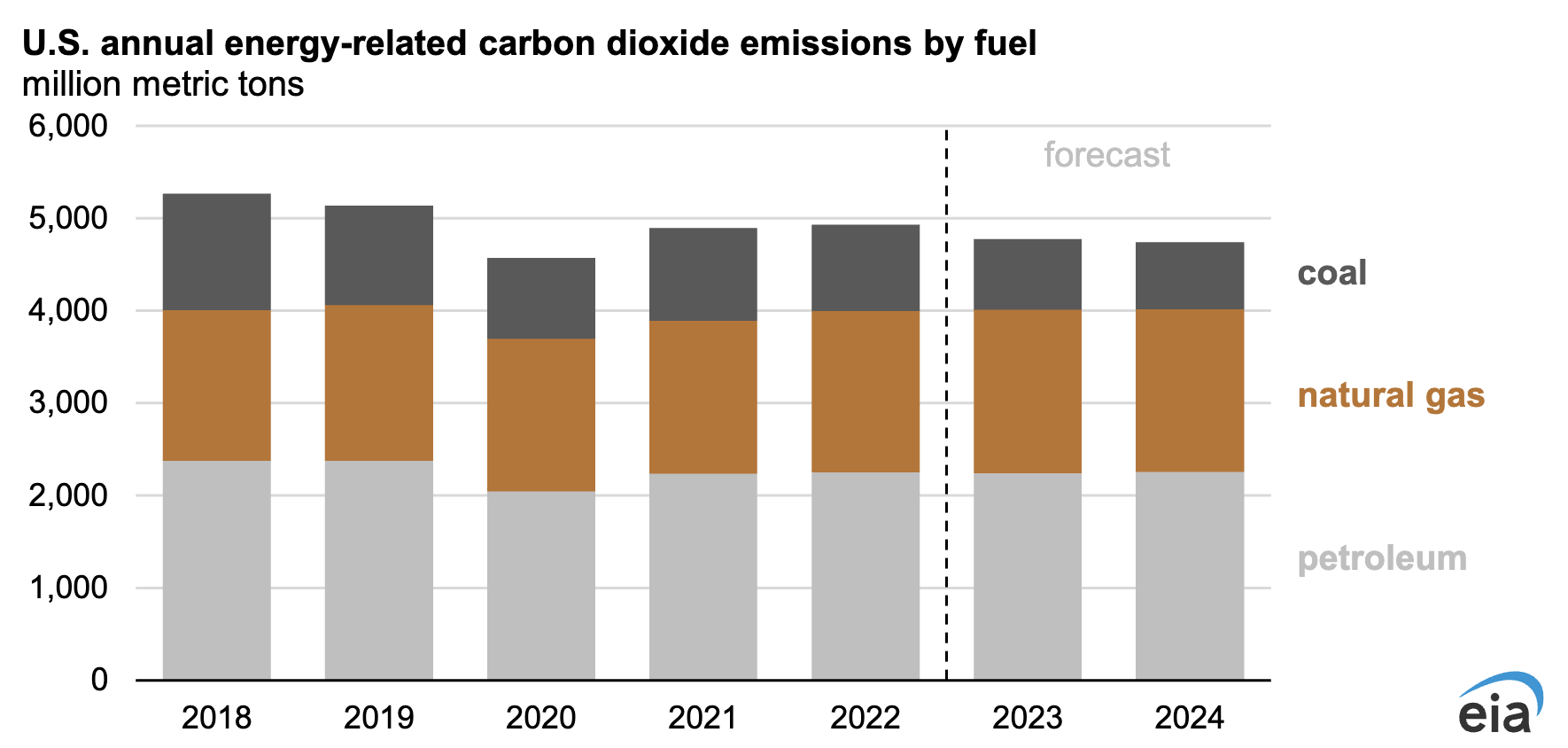
Almost half of U.S. CO2 emissions result from petroleum consumption, primarily by the transportation sector. In 2023, we estimate that petroleum emissions will remain relatively unchanged, with rising jet fuel consumption offsetting falling gasoline consumption.
Another large source of CO2 emissions in the United States is fossil fuel-fired power generation. Natural gas has become the largest source of electricity in the United States because it is a relatively low-cost fuel. Natural gas emissions also result from its consumption in the residential and commercial sectors for space heating and in the industrial sector for manufacturing processes. We estimate that U.S. CO2 emissions from natural gas will grow by 1% in 2023 and remain relatively flat in 2024.
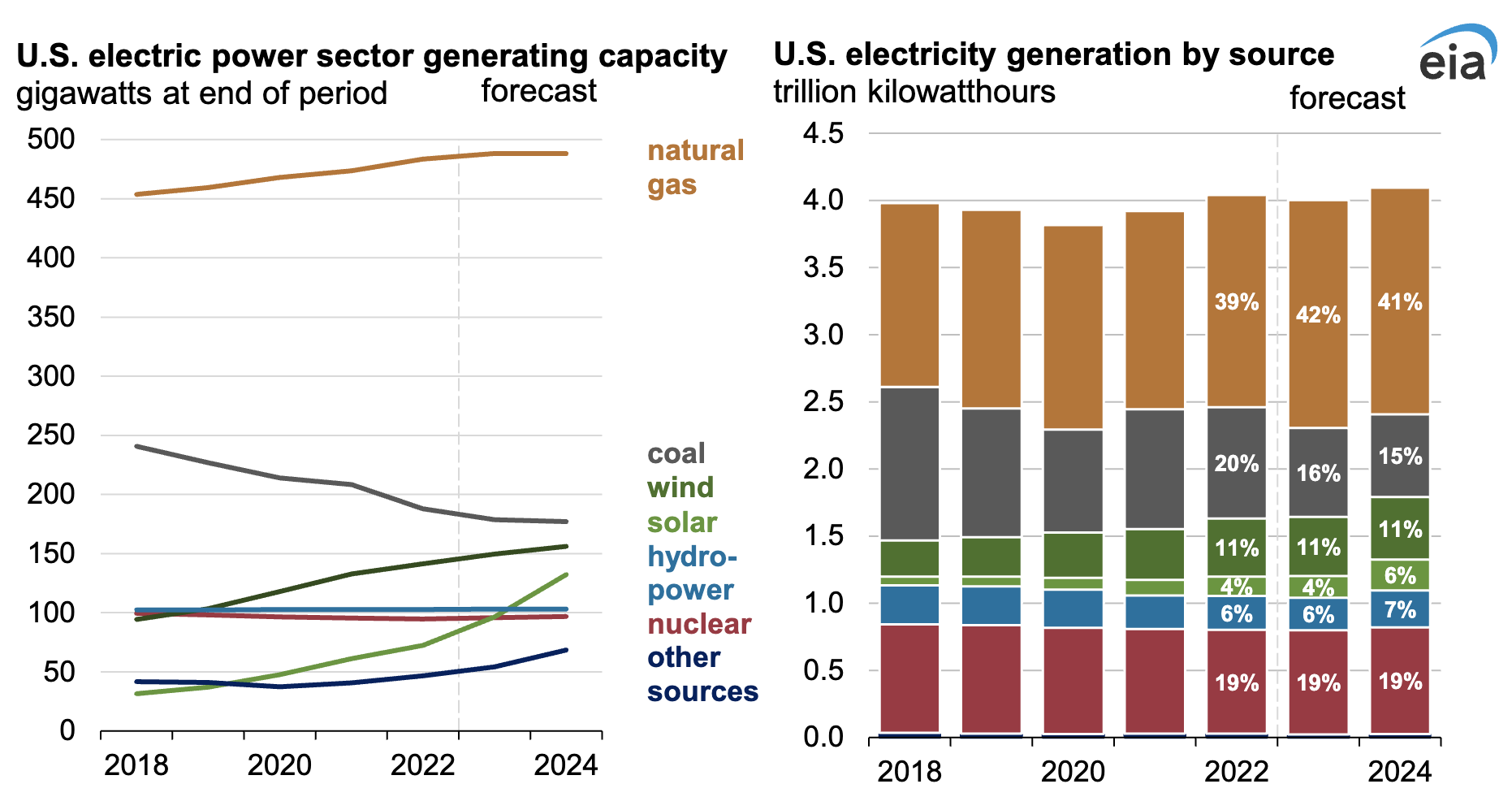
The forecast reduction in CO2 emissions is largely due to lower power generation from coal-fired power plants, which we expect to contribute to an 18% decline in coal-related CO2 emissions in 2023 and a 5% decline in 2024. The electric power sector has been retiring significant coal-fired generating capacity in response to economic competition from natural gas and new renewable generating capacity.
The electric power sector has shifted in recent years toward renewable energy sources. Much of the recent increase in renewable generation is the result of an expected 60 gigawatts of new solar generating capacity entering service during 2023 and 2024. We expect that the solar capacity increase, in addition to our forecast of increased hydropower generation and modest gains in new wind capacity, will reduce both coal-fired and natural gas-fired power generation next year.
Principal contributors: Tyler Hodge, Kevin Nakolan
Originally published on the EIA’s Today in Energy blog.
Have a tip for CleanTechnica? Want to advertise? Want to suggest a guest for our CleanTech Talk podcast? Contact us here.
CleanTechnica Holiday Wish Book
Our Latest EVObsession Video
I don’t like paywalls. You don’t like paywalls. Who likes paywalls? Here at CleanTechnica, we implemented a limited paywall for a while, but it always felt wrong — and it was always tough to decide what we should put behind there. In theory, your most exclusive and best content goes behind a paywall. But then fewer people read it!! So, we’ve decided to completely nix paywalls here at CleanTechnica. But…
Thank you!
CleanTechnica uses affiliate links. See our policy here.