By Aaron Foyer
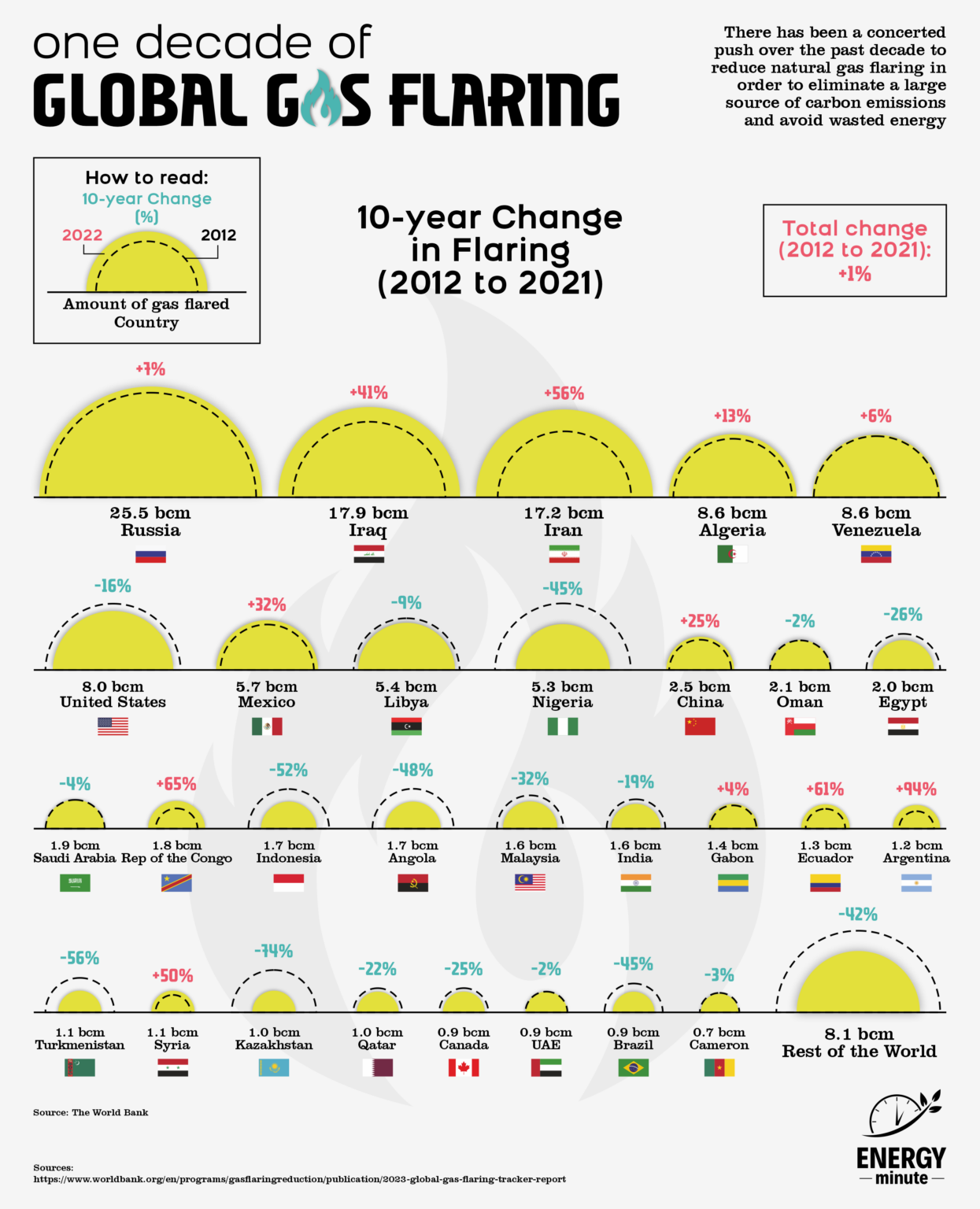
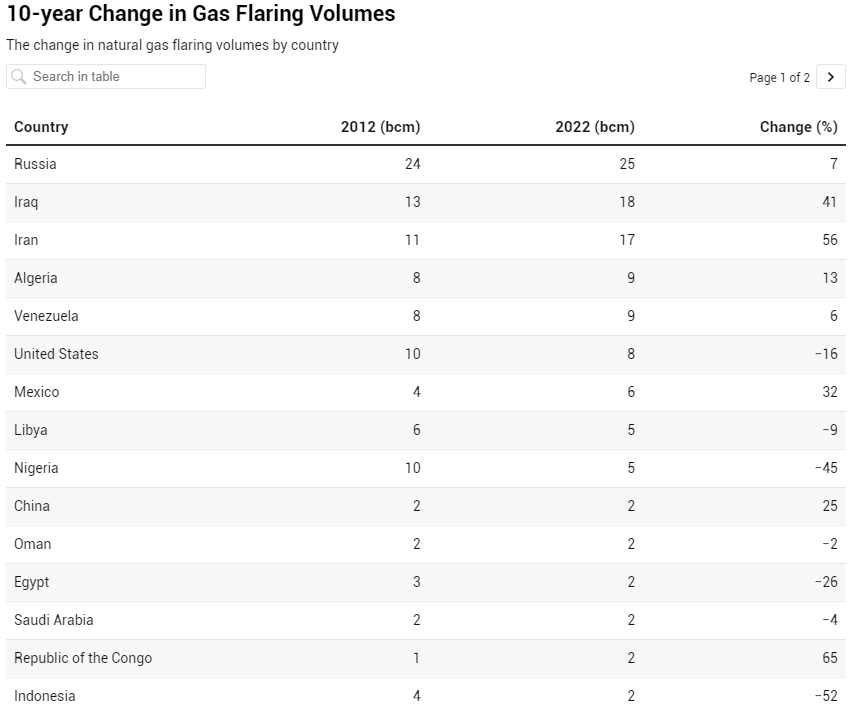
Global gas flaring is the process of burning off unwanted natural gas in the atmosphere during oil and gas production. This practice occurs for a variety of reasons, including safety, lack of infrastructure to capture the gas, regulatory practices, or economic factors. Gas flaring has significant environmental and economic implications.
Environmental Impact
- Emissions: Flaring contributes to climate change by releasing large amounts of carbon dioxide.
- Air pollution: Besides CO2, flaring can emit other pollutants, including sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), particulate matter, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which can harm human health and the environment.
- Resource waste: The gas flared is a valuable natural resource that could be used to generate energy. By flaring it, we are essentially wasting a potential source of energy.
Economic Implications
- Lost revenue: The gas that is flared could be captured and sold, providing additional revenue for countries and companies.
- Energy waste: In regions with limited access to energy, the flared gas represents a significant waste of potential energy resources.
Source: World Bank
Global Efforts to Reduce Gas Flaring
Several international initiatives and agreements aim to reduce gas flaring. For example, the World Bank’s Global Gas Flaring Reduction Partnership (GGFR) is a collaborative effort between governments, oil companies, and international organizations to reduce flaring by sharing best practices and implementing technologies to capture and utilize the flared gas. The initiative encourages transparency through reporting and aims to support regulatory frameworks that facilitate gas utilization.
Source
https://www.worldbank.org/en/programs/gasflaringreduction/global-flaring-data
Share This: