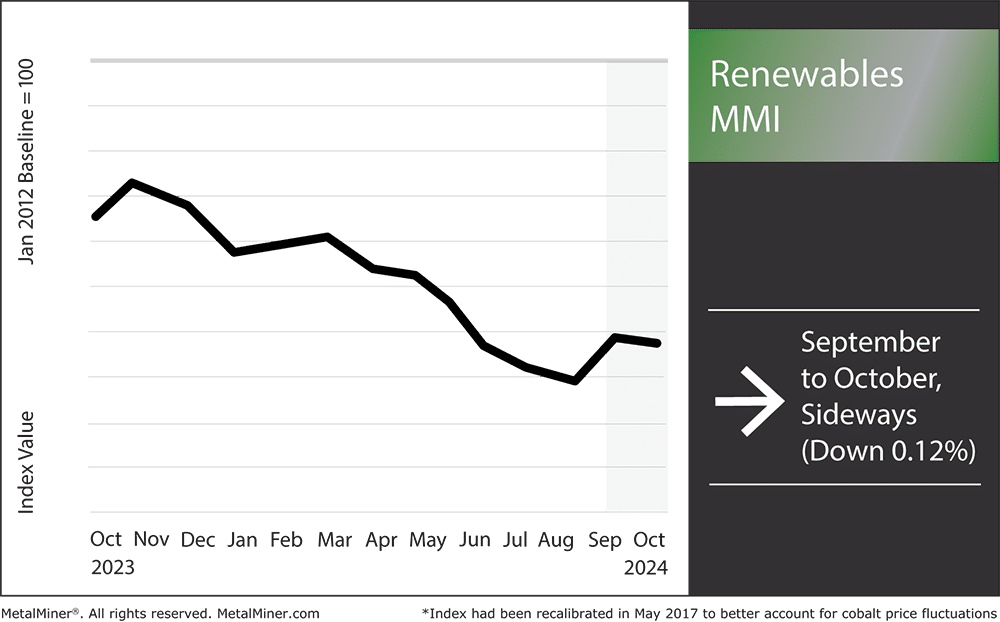
The Renewables MMI (Monthly Metals Index) slowed down its upward price action and moved sideways, edging down by 0.12%.
China Critical Minerals Restrictions Now in Full Effect
On October 1, 2024, China imposed significant restrictions on the export of critical minerals, sending ripples through global markets. These minerals, including elements like gallium, germanium, and graphite, are essential to a wide range of renewable industries, particularly those involving batteries and semiconductors.
Opt into MetalMiner’s Weekly Newsletter and keep up with the latest metal market industry news, prices and trends to stay competitive.
Global Critical Minerals Prices Rise
China’s new policies, including stricter export controls and a rare earth product tracking system, have already begun driving up global prices. Since the limits took effect, the prices of gallium and germanium, key materials for semiconductor fabrication, have increased by 8.33%. Since these minerals are essential to a variety of industries, including electronics and green technology, shortages have significant repercussions.
However, the prices of these two critical minerals aren’t the only ones that have risen. Export limitations on graphite, a crucial component of lithium-ion batteries, also threaten the manufacturing of energy storage and electric vehicle (EV) batteries.
Negative Impacts
Unfortunately, the renewable energy sector is especially susceptible to these new limitations. Because components like graphite neodymium are essential to renewable energy, supply shortages might lead to lags in production, increased prices and the postponement of important projects.

For instance, wind turbine makers utilize rare earth magnets to increase turbine efficiency. However, production delays are practically a given as China tightens its control over the export of these components, which might halt attempts to supply the rising demand for wind energy worldwide. Similarly, the graphite-dependent EV market may witness price increases as Chinese-based manufacturers find ingredients more challenging to source.
These limitations also highlight potential supply chain weaknesses. With China controlling a large portion of the world’s vital mineral supply, industries worldwide are becoming increasingly aware of the perils associated with relying on a single source.
Positive Opportunities for Innovation
Even as these restrictions bring immediate challenges, they also present opportunities for innovation and diversity. For example, the renewable energy industry can now accelerate efforts to find alternative resources to reduce its reliance on Chinese-controlled supply chains.

In response to the limits, businesses and governments are likely to increase investments in research and development to discover substitutes or other sources for these essential elements. With any luck, these can help them better meet the demands of clean energy technology.
This situation may also encourage the growth of a circular economy, which focuses more on recycling and reusing essential minerals from existing products. In this way, renewable energy companies can mitigate the risks of relying on unpredictable exports by developing closed-loop supply networks.
MetalMiner Insights is your key to risk-mitigating strategies, view our full catalog of covered metals.
The Path Ahead
With more resilient and sustainable supply chains, the renewable energy sector could emerge stronger in the long run. While the future remains uncertain, the drive for clean energy continues, and the way businesses respond to regulations on critical minerals will shape the course of the global energy transition.
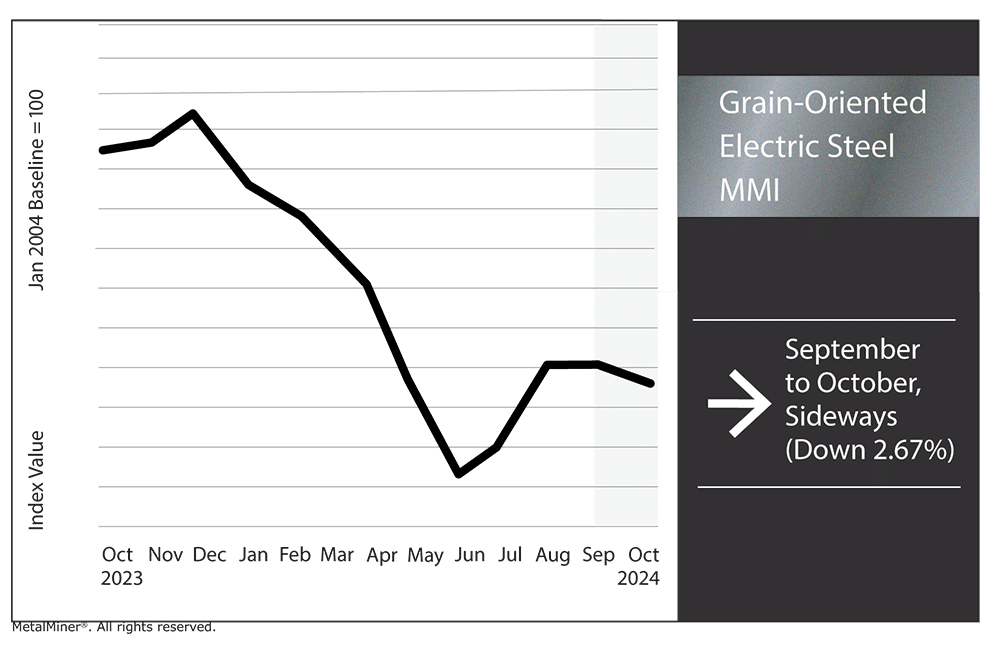
Grain-Oriented Electrical Steel MMI
The Grain-Oriented Electrical Steel MMI (GOES MMI) moved sideways again month-over-month. However, instead of trading flat, the index moved down 2.67% between September and October.
Renewables MMI: Noteworthy Price Shifts
Make informed metal sourcing decisions. Access MetalMiner’s free Monthly Metals Index report to understand economic metal price drivers through monthly price charts and expert analysis.
- Neodymium prices rose by 6.77% to $75,097.45 per metric ton.
- Chinese cobalt cathodes prices moved sideways, dropping by 1.97% to $22.62 per kilogram.
- Chinese silicon prices also moved sideways, dropping by 1.25% to $479.44 per metric ton.
- Finally, U.S. steel plate prices dropped significantly, falling 7.21% to $978 per short ton.




