By Aaron Foyer
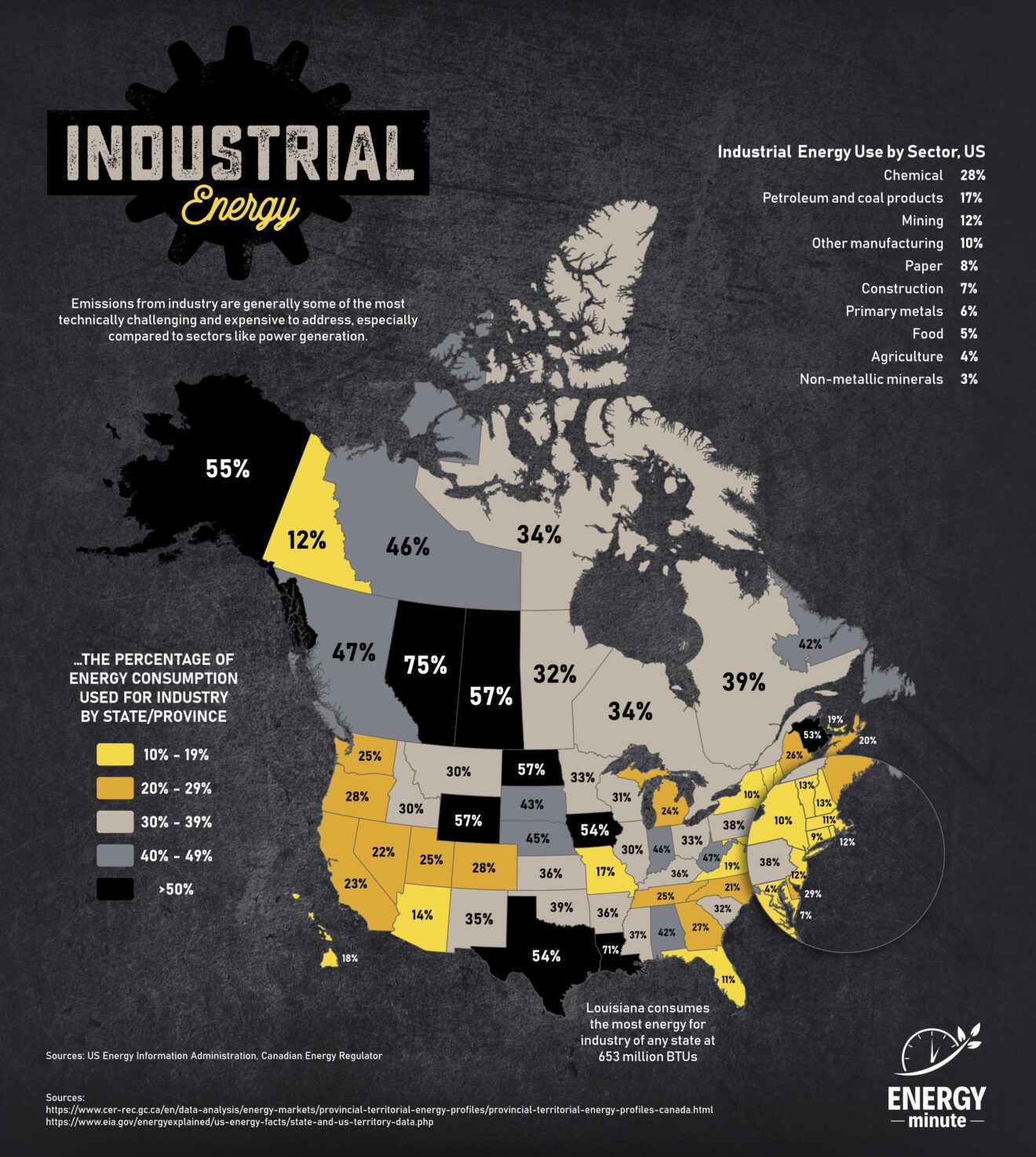
Courtesy of ENERGYminute
See more articles and infographics from ENERGYminute HERE
Energy used in industry is a significant aspect of global energy consumption, encompassing a diverse range of activities, each with its own energy requirements. Here’s an overview:
Types of Energy Used
Industrial energy consumption involves various types of energy sources. The most common are:
- Fossil fuels: Coal, natural gas, and oil are widely used, especially in heavy industries like steel and cement production.
- Electricity: Used across various industries for powering machinery, lighting, and other electrical equipment.
- Industrial heat: The large-scale generation and application of heat energy used in manufacturing and processing operations within various industries.
Major Energy-Consuming Industries
- Manufacturing: This includes steel, chemicals, paper, and automotive industries, among others, and is typically the most energy-intensive sector.
- Construction: Uses energy for producing building materials and operating construction equipment.
- Mining and quarrying: Energy is used for drilling, digging, and processing minerals.
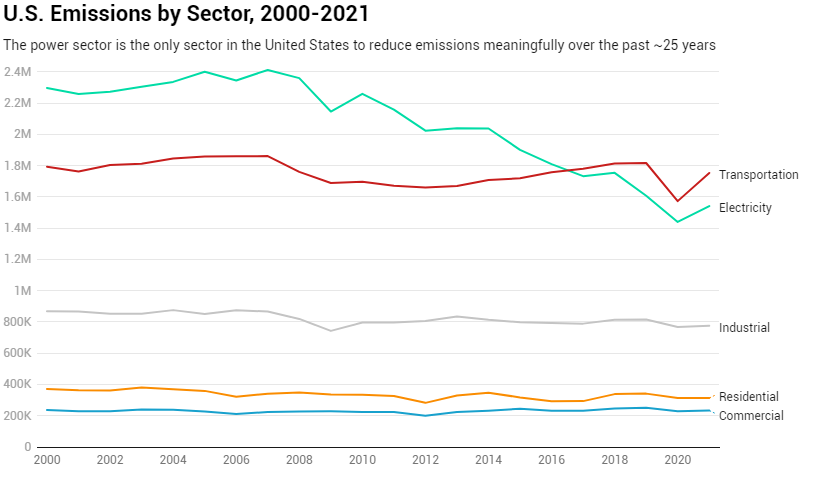
Source: US Environmental Protection Agency – Created with Datawrapper
Decarbonizing Industry
Industrial emissions are some of the hardest to decarbonize, for several reasons.
- High energy demand: Many industrial processes require substantial amounts of energy, often at high temperatures, making it difficult to substitute fossil fuels with renewable energy sources.
- Technologies: Current technologies for low-carbon and renewable energy sources may not always meet the specific needs of certain industrial processes, especially those requiring intense heat or consistent, reliable power supply.
- Economics: Transitioning to greener technologies often involves high initial costs and can be economically challenging, particularly for industries operating on thin margins or in competitive markets.
- Infrastructure: Decarbonizing may require substantial changes in infrastructure, both within industries and in the wider energy supply chain, posing logistical and financial challenges.
- Markets: The competitive nature of global markets can make it challenging for individual companies to invest in decarbonization without risking their market position, especially if competitors do not face similar environmental regulations.
These challenges require coordinated efforts across technological, economic, and policy fronts to achieve meaningful progress in decarbonizing industry.
Sources:
https://www.cer-rec.gc.ca/en/data-analysis/energy-markets/provincial-territorial-energy-profiles/
https://www.epa.gov/ghgemissions/inventory-us-greenhouse-gas-emissions-and-sinks-1990-2021
https://www.eia.gov/state/seds/data.php?incfile=/state/seds/sep_sum/html/rank_use_capita.html&sid=US
Share This:



