The Weir Group has completed a comprehensive study that highlights a significant opportunity to reduce energy use and emissions in comminution by leveraging three alternative technology combinations.
The study, presented by Paula Cousins, Chief Strategy and Sustainability Officer at Weir, during a COP28 panel discussion hosted by the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry of Japan and moderated by the World Business Council for Sustainable Development (WBCSD), showed that replacing conventional technology with innovative new solutions can cut energy use by 40% while also avoiding 50% of CO2e emissions.
Weir’s study focuses on comminution – the crushing process that turns big rocks into tiny particles to expose the entrapped mineral so that it can be extracted later in the mining process. Comminution is the most energy intensive stage of a typical mine site process. It is already electrified and is responsible for at least one-third of an average mine’s energy use and CO2e emissions1 and globally consumes around 3% of the world’s electrical power, according to studies.
The study is the first to use WBCSD’s Avoided Emissions Guidance to study mining processes and the avoided emissions results have been independently assured by SLR Consulting Limited, Weir says. Three of Weir’s technology combinations were evaluated against a conventional comminution circuit design for an archetypal mine processing 15 Mt/y of copper ore in Chile. All three of the technology combinations are shown to yield sizeable benefits versus the traditional circuit.
In the optimal combination, the comminution process consumes around 40% less energy and can avoid up to 50% of CO2e emissions. Importantly, there is no trade off elsewhere, as the redefined process uses less water too, according to the study.
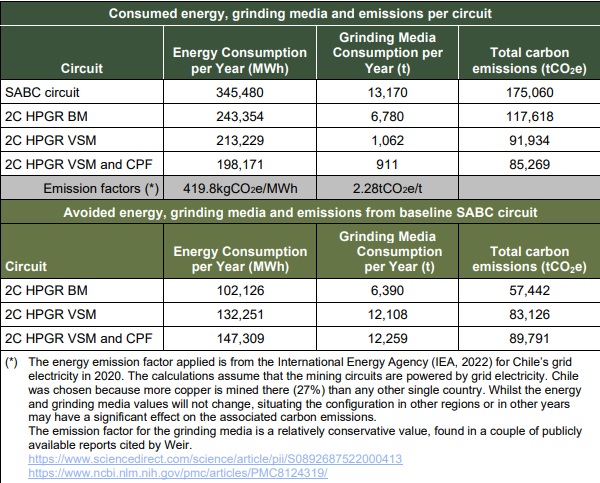
Each circuit is based on a ‘rock to recovery’ system boundary – reducing rock direct from the mine to a size that enables the mineral to be recovered. The four configurations are:
- Conventional comminution circuit based on a Semi-Autogenous Grinding (SAG) mill and ball mill (SABC circuit);
- Weir High Pressure Grinding Roller (HPGR) replacing the SAG mill at the initial grinding stage (2C HPGR BM);
- HPGR, plus vertical stirred mill (VSM) replacing the ball mill (2C HPGR VSM); and
- Addition of a coarse particle flotation (CPF) unit (2C HPGR VSM and CPF).
These assessments focus on the use-phase of the life-cycle only; other life-cycle phases have been excluded because previously studies have shown these to be immaterially small across all comparisons (<1% of energy and emissions impact). Assessments have been made using a “year-on-year” timeframe approach. Comparative impacts have been assessed only in terms of energy use, grinding media consumption, and associated emissions, since other environmental trade-offs were deemed immaterial for comparison.
Given its energy intensity, the decarbonisation opportunities in comminution are huge, with the basic comminution process not having changed significantly for many decades, Weir says.
The company is collaborating with customers and other partners to redefine the process, developing innovative combinations of proven technologies to make significant improvements to efficiency and environmental performance.
Cousins said: “The need for technology solutions in mining is compelling – the world needs more transition metals to achieve net zero, but the mining industry needs to extract these using significantly less energy and water.
“By adopting a systems-based approach to technology collaborations, we can help the mining industry scale up and clean up at the same time.”




