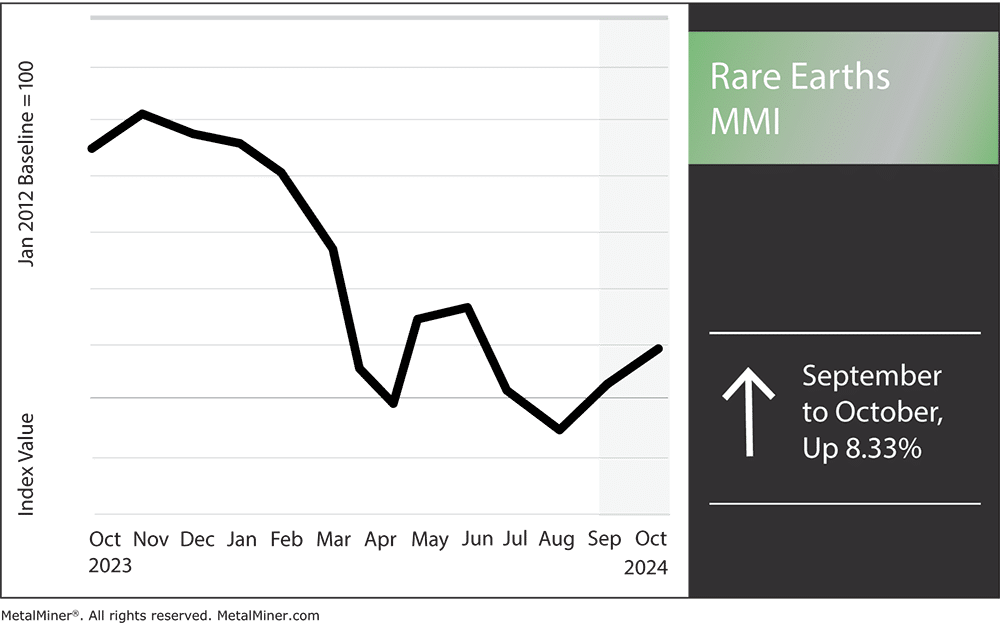
The Rare Earths MMI (Monthly Metals Index) witnessed another sharp rise in price action month-over-month, this time increasing by 8.33%. The main culprit behind the bullish momentum was China’s rare earths export restriction, which officially went into effect on October 1. The rare earths market could continue to experience volatility with the new restrictions in place. However, the market will continue to battle oversupply in the long run due to Chinese overproduction.
China’s October 1 Rare Earths Restrictions
On October 1, 2024, China imposed sweeping restrictions on rare earth exports. As the world’s largest producer of rare earths, China’s actions triggered fears and shockwaves in global markets, raising concerns across industries that depend on these critical materials.
The new limitations have already increased volatility. Global rare earth prices dropped by 20% months earlier due to overproduction and a supply surplus in China. However, as Beijing tightens exports, the market is feeling the strain, and prices are starting to climb again.
Analysts expect these new laws to drive up prices in the upcoming months as supply constraints loom, particularly in industries like electric vehicles and renewable energy, which depend heavily on rare earths. Historically, rare earth export limitations from China led to price surges. For example, after China imposed similar export restrictions in 2011, prices soared to around $67,000 per metric ton.
Enjoying this article? MetalMiner’s monthly MMI report gives you rare earth price updates, market trends and industry insight, along with insights for 9 other metals industries. Sign up for free.
Impact on U.S. Rare Earths Buyers
Reducing the United States’ reliance on Chinese rare earths has proved a constant challenge. Despite ongoing efforts to diversify supply chains, China continues to have a strong position in the market. U.S. businesses are currently dealing with longer lead times, greater costs and possible supply interruptions. This is proving especially problematic for sectors like defense, where the production of radars, communication systems and precision-guided missiles depends on access to rare earths.
Meanwhile, U.S. businesses continue to look for new ways to lessen the effects of China’s activities, such as finding alternate supplies of rare earths. Nations with substantial rare earth reserves, like Australia, are stepping up to close the shortage. However, creating alternative supply networks takes time. In the near term, increased prices and less availability will put financial pressure on many U.S. businesses.
The Ripple Effect on the U.S. Technology Industry
China’s new limitations could heavily impact the U.S. technology sector. Rare earth elements are critical to many tech products, such as computers, cellphones and electric car batteries. As such, tech giants like Google, Samsung and Apple rely on a steady supply of these materials to maintain production levels and innovate new products.

The constraints could lead to production delays, lower profit margins and higher product prices. For example, as rare earth prices rise, the electric vehicle industry (already facing increasing demand for batteries) will likely experience even steeper price hikes. Businesses will likely pass these higher costs on to customers, potentially slowing the broader adoption of environmentally friendly technologies like wind turbines and electric vehicles.
The technology industry has long relied on just-in-time supply chains, where materials arrive precisely when needed. However, China’s rare earth restrictions could force many companies to rethink their approach. This could potentially lead to stockpiling and longer-term contracts with suppliers from other regions, further driving up costs.
Stay alert to rapid rare earths market shifts and make better timed purchasing decisions with MetalMiner Insights’ instant alerts. Ready to learn more?
The Broader Implications for Rare Earths Prices
China’s export limitations on rare earths carry geopolitical ramifications along with economic ones. By tightening control over essential materials, Beijing is asserting its dominance in a critical global supply chain, forcing the rest of the world to scramble for alternatives. As countries like the U.S. and EU work to secure their supply chains, international trade dynamics may shift significantly.

Despite the growing momentum to break China’s monopoly on rare earths, the path forward remains unclear. Although the U.S. has made strides in boosting its own rare earth production, building a supply chain that meets demand will take years. In the meantime, U.S. buyers must navigate a challenging and increasingly costly market environment.
Rare Earths MMI: Noteworthy Price Shifts
Get a competitive edge in challenging rare earths market conditions. Learn game-changing metal industry insights by opting into MetalMiner’s free weekly newsletter.
- Dysprosium oxide rose by 4.65%, bringing prices to $250.60 per kilogram.
- Neodymium prices went up by 6.77%, settling at $75,097.45 per metric ton.
- Yttrium prices moved sideways, dropping a slight 0.3% to $28.71 per kilogram.
- Finally, terbium metal prices rose by 10.54% to $1033.43 per kilogram.




